The concept of co charge has emerged as a revolutionary approach to energy management and charging infrastructure, fundamentally transforming how we think about shared charging resources. Co charging represents a collaborative charging ecosystem where multiple users, devices, or systems share charging infrastructure, costs, and resources to optimize efficiency and reduce overall energy expenses. This innovative approach has gained significant traction across various industries, from electric vehicle charging networks to portable device charging stations and industrial applications.
In today’s rapidly evolving energy landscape, co charge systems have become increasingly important as organizations and individuals seek more sustainable, cost-effective charging solutions. The collaborative nature of co charging allows multiple stakeholders to benefit from shared infrastructure while reducing individual costs and environmental impact. This shared approach to charging infrastructure represents a significant shift from traditional single-user charging models, offering enhanced flexibility and scalability for modern energy needs.
Understanding Co Charge Technology and Infrastructure
Co charge technology operates on the fundamental principle of resource sharing and collaborative energy distribution. These systems are designed to intelligently manage charging loads across multiple devices or users, ensuring optimal power distribution while maintaining system stability and efficiency. The technology behind co charging involves sophisticated load management algorithms, smart grid integration, and advanced monitoring systems that can dynamically adjust charging parameters based on demand and availability.
The infrastructure supporting co charge systems typically includes shared charging stations, intelligent power distribution units, and centralized management software that coordinates charging activities across the network. These systems can automatically prioritize charging requests, balance power loads, and optimize energy consumption patterns to maximize efficiency. Modern co charge installations often incorporate renewable energy sources, battery storage systems, and grid-tie capabilities to further enhance their sustainability and cost-effectiveness.
Key components of co charge infrastructure include smart charging controllers that can communicate with connected devices, load balancing systems that prevent power overloads, and user management interfaces that allow for scheduling and monitoring of charging activities. The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology enables real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data-driven optimization of charging operations. For businesses exploring these solutions, a QBO test drive can provide valuable insights into how co charging systems integrate with existing financial and operational management systems.
Benefits and Advantages of Co Charge Systems
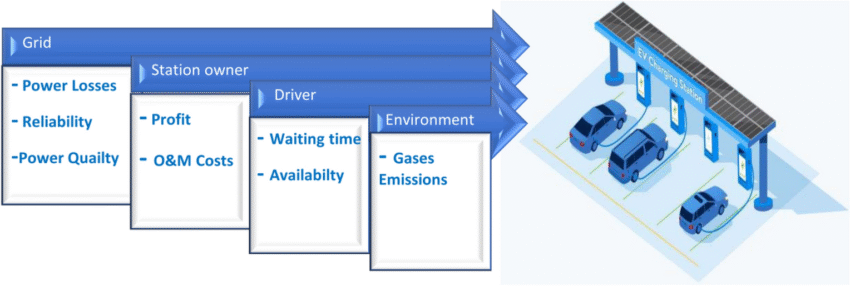
The implementation of co charge solutions offers numerous advantages that make them attractive to both commercial and residential users. One of the primary benefits is cost reduction through shared infrastructure expenses, where multiple users contribute to the installation, maintenance, and operational costs of charging systems. This collaborative approach significantly reduces the per-user cost compared to individual charging solutions, making advanced charging technology accessible to a broader range of users.
Energy efficiency represents another crucial advantage of co charging systems. By optimizing power distribution across multiple devices and implementing smart load management, these systems can reduce overall energy consumption while maintaining optimal charging performance. The ability to schedule charging during off-peak hours, integrate renewable energy sources, and implement demand response strategies further enhances the efficiency and environmental benefits of co charge installations.
Co charge networks also provide enhanced flexibility and scalability compared to traditional charging solutions. Users can access charging resources across multiple locations within the network, reducing range anxiety for electric vehicle users and providing backup charging options for critical applications. The scalable nature of these systems allows for easy expansion as demand grows, making them ideal for growing businesses and evolving energy needs.
| Benefit Category | Specific Advantages | Impact Level |
|---|---|---|
| Cost Efficiency | Shared infrastructure costs, reduced per-user expenses | High |
| Energy Management | Smart load balancing, peak demand reduction | High |
| Accessibility | Multiple location access, network availability | Medium |
| Scalability | Easy expansion, modular design | High |
| Environmental | Renewable integration, reduced carbon footprint | Medium |
Co Charge Implementation Strategies
Successful implementation of co charge systems requires careful planning, stakeholder coordination, and technical expertise. Organizations considering co charging solutions must first conduct a comprehensive needs assessment to determine charging requirements, user patterns, and infrastructure capabilities. This assessment should include analysis of peak demand periods, user behavior patterns, and existing electrical infrastructure capacity.
The planning phase should also consider the selection of appropriate co charge technology, including charging station types, power management systems, and user interface requirements. For applications requiring higher voltage systems, integration with specialized equipment like charger 24v units may be necessary to meet specific power requirements. The choice of technology should align with long-term growth plans and compatibility with existing systems.
Implementation strategies should address user onboarding, training requirements, and ongoing support needs. Successful co charge deployments often include comprehensive user education programs, clear usage policies, and responsive technical support systems. The implementation process should also consider integration with existing business systems, billing procedures, and operational workflows to ensure seamless adoption.
Key Implementation Steps:
- Site Assessment and Planning: Evaluate electrical capacity, physical space requirements, and user accessibility needs
- Technology Selection: Choose appropriate co charge systems based on power requirements and user needs
- Infrastructure Installation: Install charging hardware, electrical connections, and network infrastructure
- System Integration: Connect co charge systems with existing management and billing systems
- User Training and Support: Provide comprehensive training and ongoing technical support
- Performance Monitoring: Implement monitoring systems to track usage, efficiency, and maintenance needs
Co Charge Applications Across Industries
The versatility of co charge technology has led to its adoption across numerous industries and applications. In the transportation sector, electric vehicle charging networks represent one of the most visible applications of co charging principles. These networks allow multiple electric vehicle owners to share charging infrastructure, reducing costs while providing widespread charging access. Fleet operators particularly benefit from co charging systems that can manage charging schedules for multiple vehicles while optimizing energy costs and operational efficiency.
Manufacturing and industrial facilities increasingly rely on co charge systems to manage power distribution for electric equipment, tools, and vehicles used in their operations. These systems can coordinate charging activities to avoid peak demand charges while ensuring that equipment is always ready for use. The ability to prioritize critical equipment charging while managing overall power consumption makes co charging particularly valuable in industrial environments.
Commercial and retail establishments are adopting co charge solutions to provide customer charging services while managing operational costs. Shopping centers, office buildings, and hospitality venues use these systems to offer charging amenities while controlling energy expenses through smart load management and user fee structures. The integration of co charging with building management systems allows for sophisticated energy optimization strategies.
Industry-Specific Applications:
- Transportation: Electric vehicle charging networks, fleet charging management, public transit charging
- Industrial: Equipment charging coordination, warehouse electric vehicle charging, manufacturing tool charging
- Commercial: Customer charging services, employee vehicle charging, building energy management
- Residential: Community charging systems, apartment complex charging, neighborhood charging networks
- Healthcare: Medical equipment charging, emergency vehicle charging, facility backup power management
Technical Specifications and Requirements
Understanding the technical requirements of co charge systems is essential for successful implementation and operation. These systems typically operate on various voltage levels, from standard 120V/240V residential connections to high-voltage industrial applications. The power management capabilities of modern co charge systems allow for dynamic load balancing across multiple charging points while maintaining system stability and safety.
Communication protocols play a crucial role in co charge system functionality, with most modern systems supporting multiple communication standards including Ethernet, Wi-Fi, cellular, and specialized charging protocols like OCPP (Open Charge Point Protocol). These communication capabilities enable remote monitoring, control, and integration with broader energy management systems.
Safety features are paramount in co charge installations, with systems incorporating ground fault protection, overcurrent protection, temperature monitoring, and emergency shutdown capabilities. Modern systems also include user authentication features, billing integration, and usage tracking capabilities to support shared charging operations. The integration of smart metering technology allows for accurate usage tracking and fair cost allocation among users.
Technical Specification Categories:
- Power Requirements: Voltage levels, current capacity, power factor considerations
- Communication Systems: Network protocols, data transmission, remote monitoring capabilities
- Safety Features: Protection systems, emergency procedures, user safety measures
- User Interface: Access control, payment systems, usage tracking
- Integration Capabilities: System compatibility, data exchange, third-party integration
Co Charge Cost Analysis and ROI Considerations
The financial aspects of co charge implementation require careful analysis to ensure positive return on investment and sustainable operations. Initial installation costs vary significantly based on system size, complexity, and site requirements, but the shared nature of co charging allows these costs to be distributed among multiple users or stakeholders. This cost-sharing approach often makes advanced charging technology accessible to organizations that might not justify individual charging installations.
Operational costs for co charge systems include electricity expenses, maintenance costs, and system management fees. However, these systems often provide significant operational savings through optimized energy usage, reduced peak demand charges, and efficient maintenance scheduling. The ability to generate revenue through user fees or shared cost structures can further improve the financial performance of co charge installations.
Long-term financial benefits of co charging include reduced total cost of ownership compared to individual charging solutions, potential revenue generation through network access fees, and increased property values for locations with quality charging infrastructure. Organizations should also consider the indirect benefits of co charging, including improved sustainability credentials, enhanced customer satisfaction, and competitive advantages in attracting environmentally conscious users.
Cost Analysis Factors:
- Initial Investment: Equipment costs, installation expenses, site preparation requirements
- Operating Expenses: Electricity costs, maintenance fees, system management costs
- Revenue Opportunities: User fees, network access charges, premium service options
- Financial Benefits: Reduced per-user costs, operational savings, potential revenue generation
- ROI Considerations: Payback periods, long-term savings, indirect benefits
Frequently Asked Questions About Co Charge
What is co charge and how does it work?
Co charge is a collaborative charging system that allows multiple users to share charging infrastructure, costs, and resources. The system works by intelligently managing power distribution across connected devices or charging points, optimizing energy usage while ensuring all users have access to charging capabilities when needed.
How much does it cost to install a co charge system?
The cost of installing a co charge system varies depending on the size, complexity, and specific requirements of the installation. Factors affecting cost include the number of charging points, power capacity requirements, site preparation needs, and integration requirements. However, the shared nature of co charging typically reduces per-user costs compared to individual charging solutions.
Can co charge systems work with existing electrical infrastructure?
Most co charge solutions are designed to integrate with existing electrical infrastructure, though some upgrades may be necessary depending on power requirements and current capacity. Professional assessment of existing electrical systems is recommended to determine any necessary modifications or upgrades needed to support co charging implementation.
What maintenance is required for co charge systems?
Co charge maintenance typically includes regular inspection of charging equipment, software updates, electrical connection checks, and user interface maintenance. Many modern co charge systems include predictive maintenance features that can identify potential issues before they cause system failures, reducing maintenance costs and improving reliability.
How do users access and pay for co charge services?
Access to co charge systems typically involves user authentication through mobile apps, RFID cards, or other identification methods. Payment options can include subscription models, per-use fees, time-based charging, or integration with existing billing systems. Many co charge networks offer flexible payment options to accommodate different user preferences and organizational requirements.
Source: For more information about co charge systems and their implementation, visit the comprehensive co charge resource center at Co Charge Solutions.
Ready to explore co charge solutions for your organization? Contact our co charge specialists today to discover how collaborative charging systems can reduce costs, improve efficiency, and support your sustainability goals. Our team can provide customized co charge assessments and implementation strategies tailored to your specific needs and requirements.